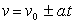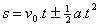Gerak adalah perubahan posisi suatu benda terhadap titik acuan. Titik acuan sendiri didefinisikan sebagai titik awal atau titik tempat pengamat.
Motion is a change in the position of an object to a reference point. Own reference point is defined as a starting point or a point where the observer.Gerak bersifat relatif artinya gerak suatu benda sangat bergantung pada titik acuannya. Benda yang bergerak dapat dikatakan tidak bergerak, sebgai contoh meja yang ada dibumi pasti dikatakan tidak bergerak oleh manusia yang ada dibumi. Tetapi bila matahari yang melihat maka meja tersebut bergerak bersama bumi mengelilingi matahari.
Motion is relative motion of an object that is highly dependent on its reference point. Moving object can be said not to move, sebgai example table which is on earth will not move by saying that there are human beings on earth. But when the sun is seen then the table moves with the earth around the sun. Contoh lain gerak relatif adalah B menggedong A dan C diam melihat B berjalan menjauhi C. Menurut C maka A dan B bergerak karena ada perubahan posisi keduanya terhadap C. Sedangkan menurut B adalah A tidak bergerak karena tidak ada perubahan posisi A terhadap B. Disinilah letak kerelatifan gerak. Benda A yang dikatakan bergerak oleh C ternyata dikatakan tidak bergerak oleh B. Lain lagi menurut A dan B maka C telah melakukan gerak semu.
Another example is the relative motion of B menggedong A and C still see B walked away from C. According to C then A and B move because of changes both the position of C. Meanwhile, the B of A does not move because there was no change in position A to B. Herein lies the relativity of motion. Object A is said to move by C was said to be moved by B. Another according to the A and B then C has made a false move.
Gerak semu adalah benda yang diam tetapi seolah-olah bergerak karena gerakan pengamat. Contoh yang sering kita jumpai dalam kehidupan sehari-hari adalah ketika kita naik mobil yang berjalan maka pohon yang ada dipinggir jalan kelihatan bergerak. Ini berarti pohon telah melakukan gerak semu. Gerakan semu pohon ini disebabkan karena kita yang melihat sambil bergerak.
Motion is quasi-stationary objects, but as if moved because of motion of the observer. The example we often encounter in everyday life is when we got the car running so that the tree is visible moving lane road. This means the tree has made a false move. Apparent movement of this tree because we are seen as moving.Pembagian Gerak
Bedasarkan lintasannya gerak dibagi menjadi 3
- Gerak lurus yaitu gerak yang lintasannya berbentuk lurus
- Gerak parabola yaitu gerak yang lintasannya berbentuk parabola
- Gerak melingkar yaitu gerak yang lintasannya berbentuk lingkaran
Sedangkan berdasarkan percepatannya gerak dibagi menjadi 2
- Gerak beraturan adalah gerak yang percepatannya sama dengan nol (a = 0) atau gerak yang kecepatannya konstan.
- Gerak berubah beraturan adalah gerak yang percepatannya konstan (a = konstan) atau gerak yang kecepatannya berubah secara teratur
Motion division
Based on the motion path is divided into 3 :
1. Straight-line motion is the motion of a straight-shaped trajectory
2. Parabolic motion is motion parabolic trajectory
3. Circular motion is the motion of a circular orbit
While based on the acceleration of motion is divided into 2 :
1. Irregular motion is the motion that the acceleration is equal to zero (a = 0) or constant velocity motion.
2. Motion changing regular motion acceleration is constant (a = constant) or the velocity of motion changed on a regular basis
Pada kesempatan ini hanya akan kita bahas tentang gerak lurus saja. Gerak lurus sendiri dibagi menjadi 2 :
On this occasion we will discuss only the straight motion. Straight-line motion itself is divided into 2:
1. Gerak Lurus Beraturan (GLB)/Straight irregular motion (GLB)
adalah gerak gerak benda yang lintasannya lurus dan kecepatannya konstan (tetap). Contoh gerak GLB adalah mobil yang bergerak pada jalan lurus dan berkecepatan tetap.
adalah gerak gerak benda yang lintasannya lurus dan kecepatannya konstan (tetap). Contoh gerak GLB adalah mobil yang bergerak pada jalan lurus dan berkecepatan tetap.
Persamaan yang digunakan pada GLB adalah sebagai berikut :
s = v.t
Keterangan :
s adalah jarak atau perpindahan (m)
v adalah kelajuan atau kecepatan (m/s)
t adalah waktu yang dibutuhkan (s)
Sebelum lebih lanjut membahas tentang gerak terlebih dahulu kita bahas tentang perbedaan perpindahan dan jarak tempuh.
Perpindahan adalah besarnya jarak yang diukur dari titik awal menuju titik akhir sedangkan Jarak tempuh adalah Panjang lintasan yang ditempuh benda selama bergerak.
motion is the motion of a straight path and velocity is constant (fixed). Sample GLB movement is a moving car on the straight path and the speed remained.
motion is the motion of a straight path and velocity is constant (fixed). Sample GLB movement is a moving car on the straight path and the speed remained.
The equation used in the GLB are as follows:
s = v.t
Description:
s is the distance or displacement (m)
v is the rate or velocity (m / s)
t is the time taken (s)
Before further discussing the first motion we discussed about the differences and the displacement distance.
Displacement is the amount measured distance from the starting point toward the end point while the mileage is the length of the path taken during the moving object.
Perhatikan gambar dibawah ini :/ Note the image below:
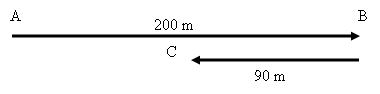
Sebuah benda bergerak dari A menuju B kemudian dia kembali ke C. Pada peristiwa di atas Pepindahannya adalah AB – BC = 200 m – 90 m = 110 m. Sedangkan jarak yang ditempuh adalah AB + BC = 200 m + 90 m = 290 m.
Apabila perpindahan dan jarak itu berbeda maka antara kecepatan dan kelajuan juga berbeda.
Kecepatan didefinisikan sebagai besarnya perpindahan tiap satuan waktu dan Kelajuan didefinisikan sebagai besarnya jarak yang ditempuh tiap satuan waktu. Perumusan yang digunakan pada kecepatan dan kelajuan adalah sama.
Karena dalam hal ini yang kita bahas adalah gerak lurus maka besarnya perpindahan dan jarak yang ditempuh adalah sama. Berdasarkan pada alasan ini maka untuk sementara supaya mudah dalam membahas, kecepatan dan kelajuan dianggap sama.
Pada pembahasan GLB ada juga yang disebut dengan kecepatan rata-rata. Kecepatan rata-rata didefinisikan besarnya perpindahan yang ditempuh dibagi dengan jumlah waktu yang diperlukan selama benda bergerak.
v rata-rata = Jumlah jarak atau perpindahan / jumlah waktu
Karena dalam kehidupan sehari-hari tidak memungkinkan adanya gerak lurus beraturan maka diambillah kecepatan rata-rata untuk menentukan kecepatan pada gerak lurus beraturan.
An object moves from A to B and then he returned to C. In the event the above displacement is AB - BC = 200 m - 90 m = 110 m. While the distance is AB + BC = 200 m + 90 m = 290 m.
If the displacement and the distance was different between the speed and the speed is also different.
The speed is defined as the amount of displacement per unit time, and Speed is defined as the amount of distance traveled per unit time. Formulation used in the speed and the speed is the same.
Because in this case that we discussed was the amount of straight-line motion displacement and distance traveled is the same. Based on this reason it is so easy for a while in discussing, speed and speed are considered equal.
In the discussion that GLB is also called the average velocity. The average velocity is defined amount of displacement is taken divided by the amount of time needed for moving objects.
v = average number of distance or displacement / total time
Because in everyday life did not permit a straight-line motion is irregular diambillah average velocity to determine the velocity of uniform straight-line motion.
2. Gerak Lurus Berubah Beraturan (GLBB)/Changed Straight irregular motion (GLBB)
Adalah gerak lintasannya lurus dengan percepatan tetap dan kecepatan yang berubah secara teratur. Contoh GLBB adalah gerak buah jatuh dari pohonnya, gerak benda dilempar ke atas.
Is the motion trajectory remains straight with acceleration and speed changes on a regular basis. GLBB example is the motion of fruit fell from the tree, the motion of objects thrown upward.GLBB dibagi menjadi 2 macam :/ GLBB divided into 2 types:
a. GLBB dipercepat/GLBB accelerated
Adalah GLBB yang kecepatannya makin lama makin cepat, contoh GLBB dipercepat adalah gerak buah jatuh dari pohonnya.
GLBB the speed is faster and faster, accelerating GLBB example is the motion of fruit fell from the tree.
Grafik hubungan antara v terhadap t pada GLBB dipercepat adalah/Graph showing the relationship between the v versus t on the accelerated GLBB
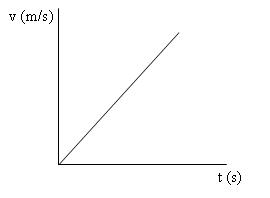
Sedangkan Grafik hubungan antara s terhadap t pada GLBB dipercepat/While Graph showing the relationship between s to t in accelerated GLBB
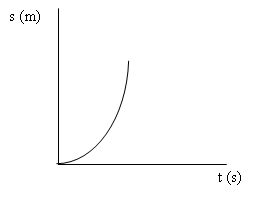
b. GLBB diperlambat/GLBB slowed
Adalah GLBB yang kecepatannya makin lama makin kecil (lambat). Contoh GLBB diperlambat adalah gerak benda dilempar keatas.
GLBB the speed is increasingly small (slow). Examples slowed GLBB is thrown upwards motion.
Grafik hubungan antara v terhadap t pada GLBB diperlambat/Graph showing the relationship between the v versus t in GLBB slowed
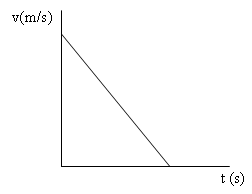
Grafik hubungan antara s terhadap t pada GLBB diperlambat/Graph showing the relationship between s to t in GLBB slowed
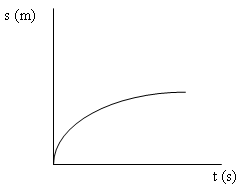
Persamaan yang digunakan dalam GLBB sebagai berikut :/The equation used in GLBB as follows:
Untuk menentukan kecepatan akhir:/To determine the final velocity:
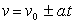
Untuk menentukan jarak yang ditempuh setelah t detik adalah sebagai berikut:/To determine the distance traveled after t seconds is as follows:
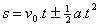
Yang perlu diperhatikan dalam menggunakan persamaan diatas adalah saat GLBB dipercepat tanda yang digunakan adalah + .
Untuk GLBB diperlambat tanda yang digunakan adalah - , catatan penting disini adalah nilai percepatan (a) yang dimasukkan pada GLBB diperlambat bernilai positif karena dirumusnya sudah menggunakan tanda negatif.
That need to be considered in using the above equation is now accelerated GLBB used signs are +.
To sign GLBB slowed used are -, an important note here is the value of acceleration (a) which is inserted in the positive value GLBB slowed because dirumusnya already using negative sign.
Latihan soal
- Sebuah bola dengan massa 10 kg dilempar keatas. Setelah mencapai titik tertinggi bola kembali jatuh ke bawah. Apabila percepatan gravitasi bumi 10 m/s2, maka (a) Jelaskan gerak apa saja yang telah dilakukan oleh bola, (b) Hitunglah waktu yang diperlukan untuk mencapai titik tertinggi, (c) Berapakah tinggi maksimum yang dapat dicapai oleh bola?
A ball of mass 10 kg is thrown upward. After reaching the highest point the ball again fell to the bottom. If the earth's gravitational acceleration of 10 m/s2, then (a) Explain what the motion was carried by the ball, (b) Calculate the time required to reach the highest point, (c) What is the maximum height that can be achieved by the ball?
- Jarak sekolah dengan rumah rudi adalah 30 km, Jika waktu masuk sekolah 07.00 dan Rudi berangkat dari rumah pukul 06.30 maka berapakah kelajuan minimum yang diperlukan Rudi supaya tidak terlambat?
Distance rudi home school is 30 km, if the time school Rudi 07.00 and left home at 06.30, what is the minimum rate required to avoid late Rudi?
- Sebuah truk bergerak dengan kecepatan 20 m/s kemudian dipercepat dengan percepatan 2 m/s2 selama 5 sekon. Berapakah kecepatan akhir truk?
A truck traveling at 20 m / s and then accelerated with an acceleration of 2 m/s2 for 5 seconds. What is the final velocity of the truck?
- Bus bergerak menuju surabaya. 10 menit pertama menempuh jarak 4 km, 10 menit kedua menempuh jarak 8 km dan 10 menit terakhir menempuh jarak 6 km. Berapakah kecepatan rata-rata bus?
Buses moving toward surabaya. The first 10 minutes to travel 4 km, 10 minutes to travel the 8 km and 10 minutes to travel 6 km. What is the average speed of the bus?
- Perhatikan grafikberikut ini:/ Consider the following graph:

Hitunglah jarak yang ditempuh benda mulai awal sampai akhir?
Calculate the distance the object from beginning to end?
 1. Langkah - langkah menyusun laporan keadaan:
1. Langkah - langkah menyusun laporan keadaan:
 b. Tentukan informasi apa yang akan dicari
b. Tentukan informasi apa yang akan dicari 2. Menyunting laporan / memperbaiki dalam sebuah naskah:
2. Menyunting laporan / memperbaiki dalam sebuah naskah: